Network Services
Network Services
🌐 Network Services
🔧 1. Common Network Services
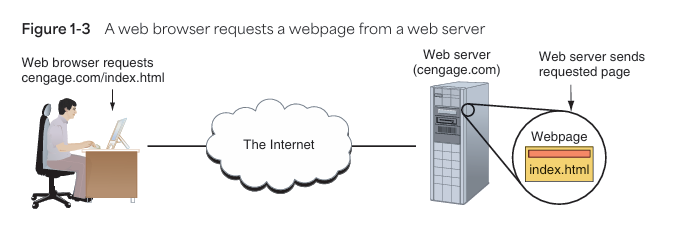
- Services are provided using a client-server model.
- A client device (e.g., web browser) requests resources from a server (e.g., web server).
- Devices can be on different networks (e.g., accessing a website over the Internet).
📡 2. Network Protocols
Protocols define how devices communicate. The most important ones are part of the TCP/IP suite:
- TCP: Reliable data delivery.
- IP: Routes packets across networks.
- Together, they allow devices to identify each other and send data correctly.
🌍 3. Web Services
- HTTP: Used for standard webpage transfers.
- HTTPS: Adds encryption using SSL or TLS for secure browsing.
- Web server software: Apache, Nginx (open-source); IIS (Windows-based).
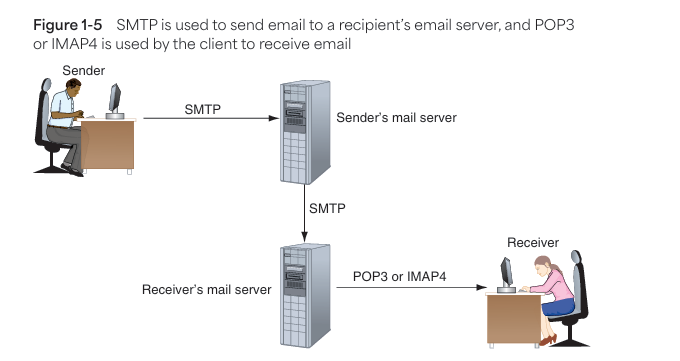
📧 4. Email Services
- SMTP: Sends email from sender to mail servers.
- POP3: Downloads email and deletes it from server.
- IMAP4: Keeps email on server for multi-device access.
- Encryption via SSL/TLS ensures secure transmission.
🌐 5. DNS (Domain Name System)
- Resolves domain names (like [www.example.com]) into IP addresses.
- Critical for accessing websites and services by name instead of numeric IPs.
🗃️ 6. Database Services
- DBMS allows data storage, access, and management.
- SQL is the primary language used for interacting with databases.
- Examples: Microsoft SQL Server, Oracle, MySQL (open source).
🔁 7. File Transfer Services
- FTP: Used for transferring files but lacks security.
- FTPS: FTP secured with SSL/TLS.
- SFTP: Secure transfer based on SSH, preferred for modern use.
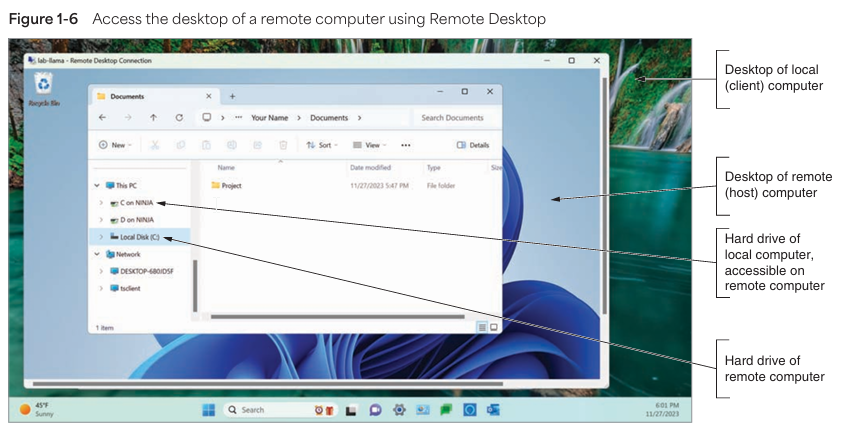
🖥️ 8. Remote Access Services
- Allow control of remote computers.
- Telnet: Insecure and outdated.
- SSH: Secure, encrypted command-line access.
- RDP: Graphical remote access on Windows.
🔐 Remote access must be secured to avoid unauthorized entry.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.